
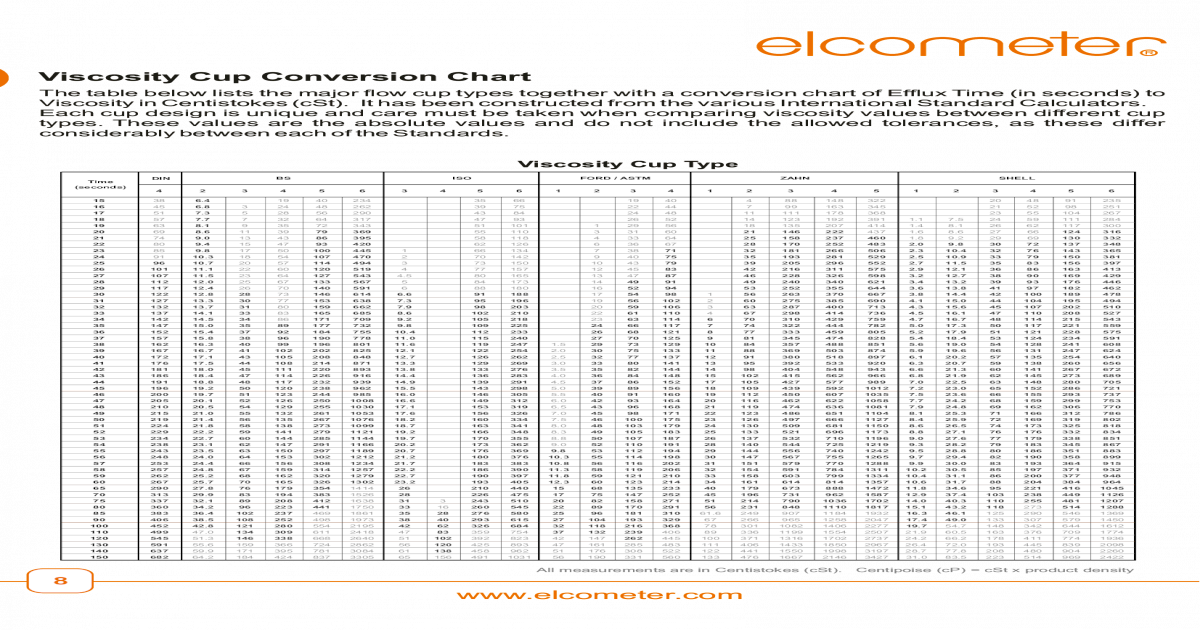
The higher the viscosity, the thicker the oil. Viscosity nowadays means a measurement of the flowability of a lubricating oil or hydraulic fluid. Several modern devices have been installed in the laboratory just for determining viscosity alone. OELCHECK principally assesses viscosity in oil samples at 40☌ and 100☌ and calculates the viscosity index from this. Since it can change when an oil is being used, it is one of the most fascinating and extensive topics in lubricant analytics. It is also dependent on temperature and can be infl uenced by special additives. It plays the decisive role in the choice of accompanying lubricant as it describes its fl uid characteristics. Viscosity is the most important physical characteristic of an oil. We often post articles and other news on our LinkedIn page, so please go and follow to keep up to date or for any pump queries you may have please contact us.The single most important physical characteristic of any oil Viscosity Comparison (centipoise 20 degrees C)Ĭentipoise (cP) = Centistokes (cSt) x S.G.Ĭentistoke (cSt) = Centipoise (cP) / S.G. There are ways to calculate (or ascertain from charts) but that is beyond the remit of this paper, so for practical purposes:Īssoma pump can handle is 150 cP (due to torque transmission through the magnets)Ĭrest can handle is 300 cp (under certain circumstances higher values may be tolerated Anything over 25cP will have a significant effect on the performance of a centrifugal pumps. Viscosity will have significant effects on flow rates and pressure capabilities of centrifugal pumps as well shaft torque and available power, the efficiency will obviously be lower. When shear is applied to non-Newtonian fluids, the viscosity of the fluid changes (e.g. Non-Newtonian fluids are the opposite of Newtonian fluids. In simple terms, a Newtonian fluid’s viscosity remains constant, no matter the amount of shear applied for a constant temperature (e.g. Kinematic viscosity is used to measure Newtonian liquids, dynamic viscosity for non-Newtonian liquids. Therefore, we say that steel has a greater density than ice. They may be the same size, but the steel cube weighs more than the ice cube. Think about an 1cm3 ice cube and a 1cm3 cube of steel. The formula for the conversion is:ĭensity is the ratio of the mass (or weight) of the sample divided by the volume of the sample. Density actually provides a way to convert between a kinematic and a dynamic viscosity measurement. What’s the difference between dynamic and kinematic viscosity?Ī basic difference between the dynamic and kinematic viscosity measurements is density. The unit of measure of kinematic viscosity is Centistokes (cSt). So kinematic viscosity is the measure of a fluid’s inherent resistance to flow when no external force, except gravity, is acting on it. The other way is to measure the resistive flow of a fluid under the weight of gravity. This is dynamic viscosity and the unit of measure for dynamic viscosity is Centipoise (cP) One way is to measure a fluid’s resistance to flow when an external force is applied. When people talk about understanding viscosity, they are talking about one of two things: dynamic (also known as absolute) viscosity or kinematic viscosity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
